Cerebral Palsy FAQ
What is Cerebral Palsy (CP)?
Cerebral palsy is not a disease, it is an injury caused by a permanent brain injury or lesion, which may occur before, during, or after birth. CP is not progressive, it does not get worse as time passes. CP can be the result of the mother having certain viral illnesses during pregnancy, Rh incompatibility (a blood conflict between mother and child), premature birth, any complication during pregnancy which causes hypoxia (lack of oxygen to the brain), genetic defects, head injuries, lead poisoning, and a host of other causes. In many cases, the cause is unknown. There is no 'cure' for CP, but various types of therapies can be used to maximize the child’s potential.
Source: Cynthia Bissell
- More on CP:
- Overview by Dr. Sheena Carter
- UCPA United Cerebral Palsy Association
- How Can I Help? Information for friends and relatives of a child with cerebral palsy
Did you know that...
- Approximately 500,000 people with CP live in the U.S.; Two of every 1,000 people.
- CP occurs more often in boys that girls (1.4 boys to 1 girl).
- Cerebral Palsy is also know as "Little's Decease" after William John Little a physician who first spoke about "spastic rigidity" in newborn infants.
- Approximately one out of two children with CP develop seizures.
- Half of all kids with CP have strabismus.
- Approximately 25% - 50% of children with CP have some mental retardation.
- The cause of most CP is unknown.
Source: Most of these statistics obtained from Coping with Cerebral Palsy, Answers to Questions Parents often Ask. Second Edition, by Jay Schleichkorn, Pro-ed publishing
What are some early signs of CP?
- Poor head control after 3 months of age
- Increased muscle tone (muscle stiffness)
- Decreased muscle tone (floppy or limp muscles)
- Arching of the back
- Inability to sit up by 8 months
- Favoring one side of the body
- Increased irritability
- Feeding problems
- Continuous fisting of the hands
- Scissoring of the legs
- Pointing toes
- Tremors or seizures
- Exaggerated startle reflex
- Strabismus (crossed eyes)
Also see: Watch your baby for these signs of Developmental Problems.
Source: Cynthia Bissell
Do all kids with brain damage have CP?
Not all kids with brain damage are diagnosed with CP. It depends on the extent and location of the damage. If the damage does not effect motor control then the child will not be diagnosed with CP. They may have other issues such as mental retardation, behavior problems, learning problems, vision problems, etc, depending on where the damage is located. Also, many children who are diagnosed with CP have "normal" brain scans. This does not mean that there isn't damage, just that it isn't visible on the scan.
Source: Cynthia Bissell
How is CP Classified?
CP can be classified according to the type of movement the child makes or to the part of the body that is most involved, or both.
By type of movement:
- Spastic = rigid
- Athetoid = no muscle control
- Hypotonic = floppy
- Ataxic = balance and coordination problems
- Mixed
By involved body parts:
- Hemiplegia = one arm and one leg on the same side of the body
- Diplegia = predominantly both legs (arms also involved)
- Quadriplegia = all four extremities
Source: Cerebral palsy; A guide for care by Miller Bachrach
What is TES?
Therapeutic Electrical Stimulation (TES) is a fairly new treatment for children with CP. You may have heard of athletes using neurostimulation to build muscles by using an electrical impulse which causes a muscle contractions to build muscle bulk. This could not be used in children because of discomfort and the risk of damage to growing muscle, tendon and bone. TES is based on this idea, except it uses a low-level impulse that is not enough to cause a contraction, but is enough to increase blood flow and promote muscle growth. The treatment is done by attaching electrodes from the TES unit onto the skin over certain muscles while the child sleeps. A physical therapist specially trained to use TES, sets up a criteria for each individual child. It usually takes 3 to 6 months to see results.
TES is not a substitute for therapy. But, by promoting muscle growth and strength you can obtain faster and better progress with traditional therapy.
Source: Cynthia Bissell
What is Conductive Education (CE)?
Conductive education (CE) is a unique system of teaching and learning for children with motor disorders such as cerebral palsy and spina bifida. It is designed to improve motor skills and increase independence of many aspects of common living. It is not a cure, but a method of exercises and education which are broken down into basic functional movements. The exercises are performed intensively (5 hours per day, 5 days per week) in small groups which promotes interactivity and fun.
Conductive Education was developed at the Pet Institute in Hungary over 40 years ago and has now been widely established in England, Belgium, Australia, Israel, Holland, Hong Kong, Japan, Germany and Canada. There are other centers using principles of Conductive Education in Malta and New Zealand as well. It slowly becoming available in the United States.
- More on CE:
- NICE The National Institute of Conductive Education, UK
What is PVL?
Periventricular leukomalasia (PVL) is a type of brain injury involving an ischemic infarction (inadequate blood circulation) of the white matter of the brain adjacent to the lateral ventricles. Peri means near; ventricular refers to the ventricles or fluid spaces of the brain, leukomalasia is softening of the white matter of the brain. The softening occurs because brain tissue in this area has died. Since PVL results in the loss of vital areas of neural tissue, particularly motor fibers that control muscle movements, cerebral palsy (CP) develops in most cases. It is likely to be of a moderate to severe degree and either spastic diplegia or spastic quadriplegia, with the legs more involved than the upper extremities. Mild to severe mental retardation may occur, but some children with PVL and spastic CP have normal intelligence. Visual impairment is also possible if the injury involves the occipital region. Seizure disorders may occur but are not commonly associated with PVL.
Source: Cynthia Bissell
-
More on PVL:
What is Hippotherapy?
Hippotherapy (Therapeutic horseback riding) is a form of therapy that literally means “treatment with the help of a horse.” The primary goals are normalizing muscle tone, equilibrium reactions, head and trunk control, coordination and spatial orientation. The multidimensional swinging rhythm of the horse’s walk is transferred to the patient’s pelvis in a manner that duplicates the normal human gait. In hippotherapy the horse influences the patient rather that the rider controlling the horse. The movement of the horse is the treatment tool to achieve the goals of strength, balance and normalizing muscle tone.
Source: Cynthia Bissell
-
More on Hippotherapy:
-
Therapeutic Horseback Riding lots of links
-
North American Riding for the Handicapped Association
-
What is Dystonia?
Dystonia is the term used to describe an illness dominated by involuntary spasms and muscle contractions that induce abnormal movements and postures. Such dystonic spasms may affect one part of the body, such as the eyes, neck or a limb; a larger region, such as the neck and arms; or the whole body.
- The Dystonias: Fact Sheet
What is M.O.V.E.?
MOVE International (Mobility Opportunities Via Education) is an activity-based curriculum designed to teach students basic, functional motor skills needed for adult life within the home and community. The program is designed to build on natural body mechanics, aiming for increasing independence in sitting, standing and walking. Sixteen specific physical skills were isolated as necessary for independent mobility. Each of these has been divided into four levels of success. The program measures the student's entry level skill for each of the sixteen areas. They will then begin to work on attaining the next level within that area.
Parents are taught how to implement the MOVE curriculum in one or two day courses. Six months after the introduction of MOVE they should attend a clinic. Use of equipment is demonstrated at these courses. The curriculum includes the milestone test and explains how to set student goals. An assessment profile is used in conjunction with the curriculum to chart the student's progress.
Source: Tamara Hills
-
More on MOVE:
-
M.O.V.E. International
-
What is Botox?
Botox (Botulinum toxin) is a medication which can be injected directly into spastic muscles to reduce high tone in that particular muscle. The dose is varied according to which muscle and how severe the tightness is. Various muscles can be injected at once, although in young children this may require brief anaesthetizing. Most people notice improvement within a few days after the injections, with the results lasting for 2 - 4 months. This is usually a good time for serial casting and range of motion therapy. Over time, the effectiveness of the Botox injections seems to decrease.
Botox is not yet FDA approved specifically for children with CP, but approval has been requested and meanwhile it is being used successfully to treat spasticity. Botox almost never causes any central nervous system side effects and is known for its safety and complete reversibility. The drawback of Botox is that it only affects the muscle(s) into which it is directly injected. Children and adults with severe, overall spasticity will not benefit, as the amount needed would be far more than the maximum limit. In such cases other methods are generally recommended. Careful evaluation is recommended before choosing any method of dealing with high muscle tone.
Source: Tamara Hills
What is a Baclofen Pump?
Baclofen (Lioresal) is very commonly used as an oral medication for the treatment of spasticity. After a dose is administered, the muscles begin to relax within two hours, reaching peak effectiveness about 2 or 3 hours later, and has often lost its effect after about 8 hours. This means that the medication is taken up to four times per day. The Baclofen pump has therefore been developed to administer the medication directly into the spinal fluid, where it has maximum effect. The pump is implanted under the skin of the abdomen and a computer is programmed to release the Baclofen as desired. In most children, spasticity is decreased and they have made improvements in swallowing, speech, and other activities of daily living.
The advantages of the pump are that doses can be monitored very precisely with the computer, and the treatment is fully reversible. The pump does need to be refilled every few months, and replaced every 4 to 5 years. There is a higher risk of infection than with rhizotomies, and there is a potential for overdosing - although this is extremely rare. The pump is generally only used for children over the age of 3, who are big enough for the pump to be inserted. Careful evaluation is recommended before choosing any method of dealing with high muscle tone.
Source: Tamara Hills
What is SDR?
SDR (Selective Dorsal Rhizotomy) is a surgical procedure which is not reversible. It involves an operation under general anaesthetic, which aims to distinguish nerve branches giving unusual responses to stimuli. The nerves tested are those leading to and from spastic muscles in the legs. Any branches which reveal abnormal responses are cut by the pediatric neurosurgeon. 'Selective' means that the nerves which are cut have been selected by careful testing. 'Dorsal' refers to the top half of the nerves leading down from the brain, which is where they are cut. A Selective Dorsal Rhizotomy aims to permanently relieve spasticity in the legs, which means that walking may also improve.
The advantages of rhizotomies are that the effects are permanent. Young children have better ability to make the most of the reduction of tone, to increase their strength, and learn new movements to increase function. The disadvantages are that the effects cannot be undone, children must have good leg strength to make the most of the operation, and extensive therapy is needed afterwards. Careful evaluation is recommended before choosing any method of dealing with high muscle tone.
Source: Tamara Hills
What are Phenol blocks?
Phenol blocks are similar to Botox injections (see "What is Botox?"). Phenol has been used for the past 20 years, but has certain disadvantages when compared with Botox. The injections are quite painful, and may cause muscle tenderness for several days. There is also a small amount of permanent muscle damage caused by the injections. As a result, Phenol injections are giving way to Botox, which appears to be safer and is certainly less painful.
Source: Tamara Hills
Editor's Note: Phenol blocks last longer and are more precise than Botox and may be the treatment of choice in some cases, especially for large muscle groups. CB
What is Craniosacral Therapy?
Craniosacral Therapy is a non-invasive, gentle therapy which uses the craniosacral system of the body. This system consists of the membranes and cerebrospinal fluid that surround and protect the brain and spinal cord. The therapy uses the craniosacral system’s rhythm to detect and balance restrictions that can cause pain and dysfunction throughout the body.
Craniosacral Therapy may be used in conjunction with other therapies or when traditional therapies have proven ineffective. Craniosacral Therapy has been used in a wide range of cases from chronic symptoms to head or neck injuries following an accident. It can also be helpful for stress-related problems and various sensory disorders. The positive effects of CranioSacral Therapy have been scientifically documented.
Source: Cynthia Bissell
What is The Ketogenic Diet?
The Ketogenic Diet is a very precisely prescribed diet that is used to help control seizures in children with intractable epilepsy. The diet is very high in fat and low in sugar and carbohydrates. Calories and fluid are very strictly controlled and all food and fluids have to be precisely weighed and measured in order for the diet to work. The diet can be fairly complicated and will effect a family's daily routine
Source:
John M. Sum, MD
What is CVI?
Cortical Vision Impairment (CVI) or Cortical blindness results from injury to the brain's visual centers in the cerebral cortex. A child with cortical blindness is able to pick up visual information with her eyes, but her brain cannot process and interpret the information correctly. The result is total or partial blindness. About 25 percent of children with hemiplegia have cortical visual impairments to parts of their visual field (hemianopsia). They are able to see objects in front of them, but can't see objects to one side. Total cortical blindness is rare and usually occurs when there is extensive brain injury-for example, in children with severe quadriplegia.
Source: Children with Cerebral Palsy: A Parents' Guide
Edited by Elaine Geralis
-
More on Cortical Blindness:
-
Cortical Blindness
-
What is Cell Therapy?
Cell therapy traditionally involves the intramuscular injection of cellular tissue preparations from fetal sheep or cattle. Generally, specific tissues and organs are separated and removed from the fetus to made be available to nourish corresponding human tissues and organs. For example, fetal brain tissue preparations may be used to nourish a functionally impaired human brain. Often several fetal tissues are selected and administered to human recipients according to individual patterns of need.
What is Patterning?
Patterning is a series of exercises designed to improve the "neurologic organization" of a child's neurologic impairments. It requires that these exercises be performed over many hours during the day by several persons who manipulate a child's head and extremities in patterns purporting to simulate prenatal and postnatal movements of nonimpaired children.
-
More on Patterning:
- The Institutes for the Achievement of Human Potential
- The Doman-Delacato Treatment of Neurologically Handicapped Children (RE2709) American Academy of Pediatrics
What is an Osteotomy?
A Femoral Osteotomy, also called varus osteotomy, varus derotational osteotomy, hip osteotomy; is a surgical correction done on many children with subluxation (the ball slowly pulls out of its appropriate position in the socket) and dislocation (the ball is completely out of the socket) of the hips due to CP. The thighbone (femur) is cut usually just below the hip joint and redirected back into place. Most all varus osteotomy procedures involve implanting a plate and pins to hold and fix the osteotomy. Usually, children are placed in spica casts for 4-8 weeks after surgery. A splint or brace may be used for several months after the surgery. Bracing and therapy schedules must be adhered to. The expectation is that walking will be improved, and for non-ambulatory patients sitting will be improved.
The main factor for hip problems is the muscle imbalance. This imbalance of the muscles, specifically tight adductor muscles pulling the femur improperly producing a rotation of the hip and the ball moves slowly out of the socket. If your child does not walk the acetabulum may be very shallow. Walking actually helps the femur to sit properly in the acetabulum.
Hip subluxation / dislocation can be prevented or delayed with early and aggressive treatment. By the time a child is 2 there is a need to begin close examination of the hips. The dislocation is gradual, so the hips should be x-rayed and assessed by an orthopedic surgeon every six months. If the hips appear to be dislocating (even a small amount) a hip muscle release surgery can be performed. These muscle and tendon releases or lengthenings can prevent the hip from dislocating. Muscle releases are also done along with the osteotomy if it hasn't been previously done.
Source: Cynthia Bissell
What are Hip Muscle Releases?
(Adductor tenotomy and psoas release, hip adductor lengthening, iliopsoas release lengthening, hamstring lengthening)
The adductors pull on the bones and bring them closer to the middle of the body. They are located on the inside of the thighs. When they are too tight they make the legs scissors, which can pull the ball of the hip out of the socket. Muscle releases are an attempt to prevent the hips from dislocating. In an ambulatory child, this might be done because the feet often cross while walking.
Selected muscles of the groin are cut and allowed to retract. Which muscles are cut depends on the exact problems the child is having, extent of spasticity, if the child ambulates or not, and also on surgeon preference. Some surgeons transfer the heads of some muscle groups more toward the rear to help extend the hip. This is more extensive surgery and has not been shown to be more effective than a simple release. The illiopsoas is a tendon that contributes significantly to spastic hip dislocation. This tendon is often cut and allowed to retract. In ambulatory children only the psoas is cut while the iliacus muscle is not touched. The illiopsoas can also be transferred and sutured to the pelvis or hip joint capsule.
The hamstrings can be lengthened or cut at the same time as the other muscles are cut. The hamstrings are the large muscle group located on the backside of the thigh. The two groups of muscles, one on the inside and one set on the outside of the thigh, can become tight and contracted. Children who sit in a wheelchair all of the time are at risk for developing this contracture and at that time the legs will be so tight they will not be able to lie down flat. These tight muscles can contribute to hip subluxation, hunched posture and poor positioning. It can also lead to spinal problems as it progresses.
Source: Cynthia Bissell
What is Strabismus?
Strabismus or "cross-eye" is due to an imbalance of the eye muscles and occurs in half of all children with spastic CP.
The treatment for strabismus is either glasses or patching. If this is unsuccessful, then surgery is needed to ensure that both eyes work together for visual acuity in each eye. The surgery may need to be repeated before proper alignment is obtained (25% of children with strabismus need more that one surgery).
Source: Cynthia Bissell
-
More on Strabismus:
-
The American Association for Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus (AAPOS)
-
What is Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT)?
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (abbreviated HBOT) is a medical treatment that uses pure oxygen to speed and enhance the body's natural ability to heal. High dose oxygen therapy is an American Medical Association, FDA and Medicare approved modality. During therapy, the patient breathes pure, 100% oxygen under increased atmospheric pressure. (The air we normally breathe contains only 19-21% of this essential element.) The concentration of oxygen normally dissolved in the bloodstream is thus raised many times above normal (up to 2000%). In addition to the blood, all body fluids including the lymph and cerebrospinal fluids are infused with the healing benefits of this molecular oxygen. It can reach bone and tissue which are inaccessible to red blood cells, enhance white blood cell function, and promote the formation of new capillary and peripheral blood vessels. This results in increased infection control and faster healing of a wide range of conditions.
How can cerebral palsy children be helped? A course of oxygen therapy sessions has been shown to resolve tissue swelling after the lapse of years. It works by constricting blood vessels and interrupting the vicious cycle where oxygen lack leads to tissue swelling, which then leads to further oxygen deficiency.
Theoretically, the use of HBOT in CP, TBI, and in the very young will actually give the brain a jump-start. It also produces an ideal internal environment for the growth of new brain tissue.
Source:
Ocean Hyperbaric Center
Dr. Richard Neubauer, Medical Director
4001 Ocean Drive, Suite #105
Lauderdale-by-the Sea, Florida 33308
(954) 771-4000
1-800-552-0255
Diplomate American Board Hyperbaric Medecine
Co-Founder American College Hyperbaric Medecine
President of the Society for Freestanding Hyperbaric Oxygen Centers
www.oceanhbo.com
What is an Adeli Suit?
The beginning of 1960 is characterized by an intensive development of cosmonaut technologies with in Russia ( previously Soviet Union ) and USA. The very intensive research was provided to determine the influence of the lack of gravity and hipokinesis on the human body. It was noticed that a person surrounded by a gravityless environment displays changes within the nervous, circulatory, respiratory and musculo-skeletal systems. In 1971 in Soviet Union Prof. A.S. Barer and associates created cosmonauts suit "Penguin" which major goal was to combat the negative effects of a gravityless environment. It was first used in a "Salut "- Space Station by the Dobrowolski, Wolkow and Pacajew Team. One of the crucial components of the Suit is the system of elastic rubber bands which force the skeletal as well as cardiac muscles to work, which of a particular importance for the cosmonauts. This Suit was very crucial for the Russians who trying to prolong the stay in space. They created the suit that stimulated the workout of the human body during the space flights. During the Soviet Union break-up some of the details of the cosmonaut technologies were disclosed. The group of scientists from the Russian Aeronautic Space Agency and Russian Academy of Science decided to imply the space suit into rehabilitation of children with CP. The results of this trial were very interesting. Therefore the Pediatric Institute of Russian Academy of Science with Prof. Dr. Siemionowa as a team leader created new suit - LK-92"ADELI". This suit was created purposefully to rehabilitate the patients with CP.
The suit consisted of the vest or shoulder pads, wide belt to be worn around the hips or shorts, knee pads and shoes specially adapted to connect them with the rest of the suit. All those elements of the suit are connected with each other through the system of elastic rubber bands. They consist of either rubber, plastic elements or metal springs. On the vest, shorts, knee pads and shoes there are special attachments for the rubber bands. The rubber bands do mirror the course of the human muscles: flexors, extensors, adductors and rotators of the trunk and lower extremities. It is possible to add additional rubber band to correct the alignment of shoulder girdle, trunk, hips, knees and feet as well as for much more precise functions. The rubber bands create possibility to vertically load the body up to 40kg (80 lb.) between the shoulder girdle and feet. Practically, however no more than 15 - 25 kg ( 30 - 50 lb.) is being used.
The very important aspect of the suit is that it does not limit the voluntary movements of the child, but it does require more effort in order to create desired movement. It all depends on the tension of the rubber bands. Throughout that adjustability of the bands it is possible to externally influence the tension of the certain muscle group of the trunk and lower extremities. The suit is individually adapted to fit the patient's height. The suit does not affect the upper extremities. It is also important that the tension of the rubber bands and trough that the loading can be individually adjusted during the therapy session.
Source: REHABILITATION OF PATIENTS WITH CENTRAL MOTOR NEURON DISORDERS USING ADAPTED COSMONAUT'S SUIT LK - 92 ADELI (Janusz Koperek D.O.,L.Sadowska M.D.- Euromed medical consultants)

- More on Adeli Suit:
- About Adeli Suit Method and Treatment in Euromed
What is a SWASH brace?
A SWASH brace is one that has been made to help kids with CP learn to walk more correctly by decreasing the amount of scissoring while they walk. Scissoring is when the legs cross each other at the midline and stops us from being able to stand straight and walk more normally.
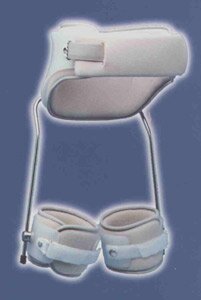
What is a Benik Vest?
Benik Vest is a special vest that is weighted to help people learn how to support their trunk and learn how to balance themselves.

What is Feldenkrais Threapy?
The Feldenkrais Method is a form of somatic education that uses gentle movement and directed attention to improve and enhance human functioning. Dr. Moshe Feldenkrais (1904-1984) developed his Method in the late 1940s after a crippling knee injury. Synthesizing his background in mechanical engineering and physics with his curiosity about linguistics, biology, human development, and athletics, Dr. Feldenkrais taught himself to walk again. This personal breakthrough led to Feldenkrais innovative contribution in showing how the body, through movement, influences mental processes. By using movement to generate sensation, The Feldenkrais Method helps re-educate the nervous system and expand options for new ways of moving. The two forms of the work include private one-to-one lessons called Functional Integration and group lessons known as Awareness Through Movement.
What are AFO's?
AFO stands for Ankle Foot Orthoses or leg braces. There are so many kinds of ankle-foot orthoses (orthosis = brace). Depending on the persons needs, braces can do various things. A minimum requirement would be to hold at least 90 degrees.

Source: http://www.pediatric-orthopedics.com/Topics/Walking_AFOs/AFO/afo.html
What are DAFO's?
DAFO stands for "Dynamic Ankle Foot Orthotic." DAFOs are specialized AFO's custom made from casts of the child's lower extremity and can be personalized with different color padding, velcro straps, and ribbon trim.

Source: http://www.dafo.com/
What is a Body Jacket?
Your body jacket is designed to help stabilise your spine, restrict movement and provide support for the trunk. Body jackets of often used for children with CP to help them maintain correct positioning such as sitting up in the wheelchair and/or to prevent or reduce scoliosis (curvature of the spine).
Jackets are custom made for the individual.

What is Scoliosis?
The spine has natural curves. These curves round our shoulders and make our lower back curve slightly inward. But some people have spines that also curve from side to side. Unlike poor posture, these curves can't be corrected simply by learning to stand up straight. On X-ray, the spine of a person with scoliosis looks more like an "S" or a "C" than a straight line.
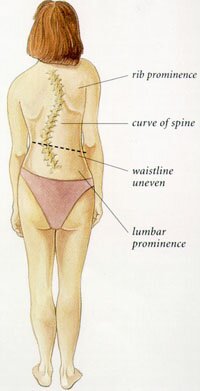
People with Cerebral Palsy have a high incidence of scoliosis which often becomes severe. This can lead to sitting balance problems for patients who are wheelchair dependent, and ultimately to respiratory and cardiac problems. Some patients can be treated with bracing, but many will benefit from surgery.
What is Myofascial Release (MFR)?
A gentle blend of stretching and massage, myofascial release therapy uses hands-on manipulation of the entire body. MFR consist of soft tissue mobilization and is enormously effective in increasing range and quality of movement. This technique is especially beneficial with patients that have spastic cerebral palsy and have limits with flexibility in their muscles and connective soft tissue.
What is Hip Dysplasia?
The hip has two major structures: a cup shaped socket called the acetabulum and the ball shaped upper end of the femur (thigh bone). Developmental hip dysplasia implies that the alignment of the head of the femur (ball) to the acetabulum (socket) is not normal. The hip may be dislocated, subluxed or dislocatable. In dislocation, the growing femoral head sits completely out of the socket. In subluxation, the growing head is partially out of the socket and if the head can be displaced by the examiner, it is considered dislocated. Treatment for the unstable hip is aimed at achieving a repositioning of the hip in the socket, maintaining the improved position, and following the childs hip development. Splints, braces, casts, tendon releases, and bony surgery are possible treatment choices for select hips.What are TheraTogs?
TheraTogs are a revolutionary orthotic undergarment and strapping system that gives clients with sensorimotor impairment an exciting new modality for improving postural alignment and stability, movement skill and precision, and joint stability.
Source: http://www.theratogs.com
This page updated 9/7/06
